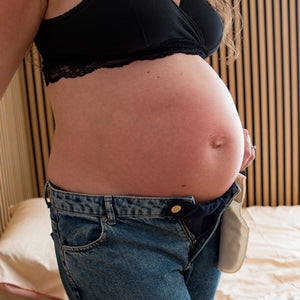
A pregnancy indicates that a mother is carrying a fertilized egg that has implanted itself in the lining of the uterus. However, in some cases, there may be more than one egg that has made it, and thus one is pregnant with twins.
Only 1.6% of all pregnancies are with two fetuses, that is, with twins. Some become pregnant with twins completely naturally, while a larger number will experience a twin pregnancy after artificial insemination or other fertility treatments.
Fraternal twins
There can be several biological reasons for becoming pregnant with twins. One possibility is through two eggs that have released from the ovaries simultaneously. This is the most common form of twin pregnancy and accounts for about 83% of all pregnancies with twins.
Each of these eggs has been fertilized by a sperm cell each, and both fertilized eggs have implanted themselves in the lining of the uterus. This also means that the fetuses can have different genders because they are two independent eggs, each of which has been fertilized separately.
If one is older, there will be a higher risk or greater likelihood that more than one egg will release. At the same time, it can also be inherited that one has a greater chance of a twin pregnancy.
Several artificial inseminations lead to twin pregnancies because, in that process, multiple eggs are often set up at once, and here two have implanted and become viable fetuses.
Identical twins
The second possibility for a twin pregnancy is rarer and constitutes the remaining 17% of twin pregnancies.
Here, it is just a single egg that is fertilized, and after this process, the egg has split into two. This results in two identical eggs, and the twins will emerge as more or less identical. Twins will share the same genetic foundation, and therefore they will always be the same gender, and their remaining appearance will be very similar.
How do you know it's twins?
Most discover that there is more than one fetus during the ultrasound scan, which takes place around the 12th week of pregnancy. This is the first scan offered by the public healthcare system in Denmark. Many choose to have a scan earlier through private means, or because they are offered scans in connection with their fertility treatment. Here, one will also be able to see if there are multiple fetuses.
In addition to scans, many will experience that their signs of pregnancy will come faster and to a greater extent if they are expecting twins. The uterus grows faster in a twin pregnancy, and therefore many will experience severe nausea and vomiting at the beginning. There will often be more symptoms associated with a twin pregnancy because the body is undergoing additional work. Many experience severe nausea, a lot of fluid retention, constipation, varicose veins, more frequent urges to urinate, and stronger back pain.
Risks of twin pregnancy
Twins are categorized based on how much they share amniotic membranes and placenta. It is best for both fetuses if they share as little as possible. If they share very unbalanced, one of the fetuses will be dominant and receive most of the nutrients.
Therefore, extra attention is always paid to twins to ensure that both fetuses develop as planned. There is indeed a greater risk of growth restriction when expecting twins. The risk is greatest with identical twins, where there is concern about twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome, where one receives plenty of nutrients while the other cannot access them and thus does not grow as planned.